|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6JNifdc-H2-Ab1tm1(HLA-DPA1*2.2-I-Aa/
HLA-DPB1*3.1-I-Ab1)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6JNifdc
|
Catalog number
|
113145
|
Aliases
|
DPA1, HLA-DPA, HLA-DP1A; DPB1, HLA-DP, HLA-DPB, HLA-DP1B
|
NCBI Gene ID
|
3113, 3115
|
Description
-
HLA-DPA1 belongs to the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. HLA-DPB1 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DPA) and a beta (DPB) chain, both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The alpha chain is approximately 33-35 kDa and its gene contains 5 exons. The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and its gene contains 6 exons.
-
The exons 1~6 of mouse I-Ab1 gene that encodes the full-length protein of I-Ab1 was replaced by a chimeric CDS sequence encoding the α chain of HLA-DP and a chimeric CDS sequence encoding the β chain of HLA-DP in B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice. The promoter sequence was derived from I-Ea gene. The following sequences were the chimeric CDS of humanized β chain including the β1 domain of human HLA-DPB1*03:01 and the β2, transmembrane, cytoplasmic domains of mouse I-Ab1 gene. The last sequences were the chimeric CDS of humanized α chain including the α1 domain of human HLA-DPA*02:02 and the α2, transmembrane, cytoplasmic domains of mouse I-Aa gene. The mouse I-A protein was not detectable in the B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice because the mouse I-Ab1 gene was disrupted.
-
Human HLA-DP was exclusively detectable in heterozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
-
B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of vaccines.
-
Application: For example, this product is used for pharmacodynamics and safety evaluation of vaccines for cancers.
Targeting strategy
Gene targeting strategy for B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice. The exons 1~6 of mouse I-Ab1 gene that encodes the full-length protein of I-Ab1 was replaced by a chimeric CDS sequence encoding the α chain of HLA-DP and a chimeric CDS sequence encoding the β chain of HLA-DP in B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice. The promoter sequence was derived from I-Ea gene. The following sequences were the chimeric CDS of humanized β chain including the β1 domain of human HLA-DPB1*03:01 and the β2, transmembrane, cytoplasmic domains of mouse I-Ab1 gene. The last sequences were the chimeric CDS of humanized α chain including the α1 domain of human HLA-DPA*02:02 and the α2, transmembrane, cytoplasmic domains of mouse I-Aa gene. The mouse I-A protein was not detectable in the B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice because the mouse I-Ab1 gene was disrupted.
mRNA expression analysis
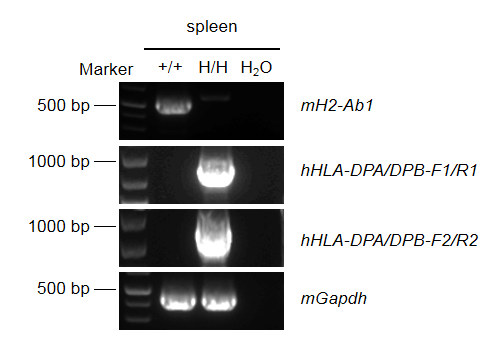
Strain specific analysis of HLA-DPA/DPB mRNA expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by RT-PCR. Spleen RNA was isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice(+/+) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice(H/H), and then cDNA libraries were synthesized by reverse transcription, followed by PCR with mouse H2-Ab1 or human HLA-DPA/DPB primers. Mouse H2-Ab1 mRNA was detectable only in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human HLA-DPA/DPB mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice but not in wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the spleen of C57BL/6 mice
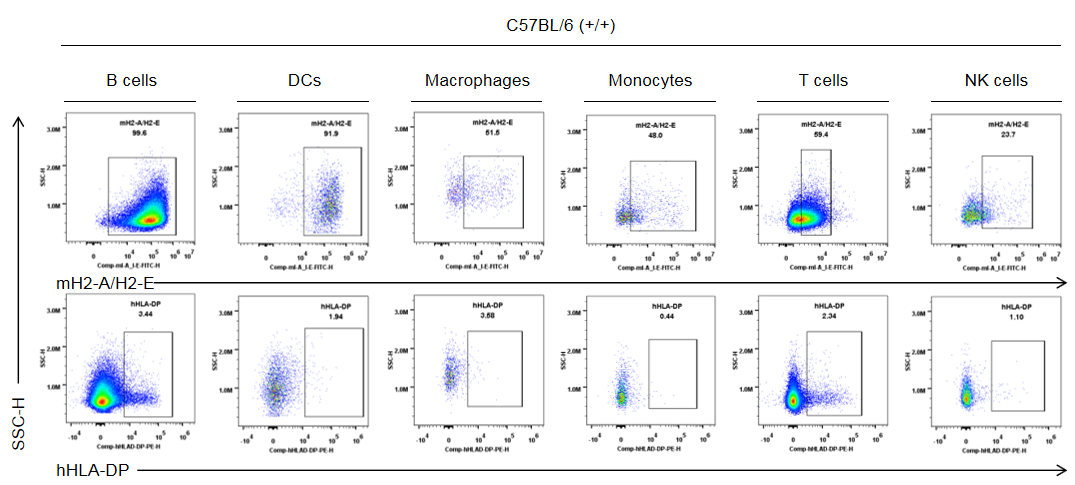
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Mouse H2-A/H2-E was only detectable in wild-type mice. Human HLA-DP was not detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the blood of C57BL/6 mice
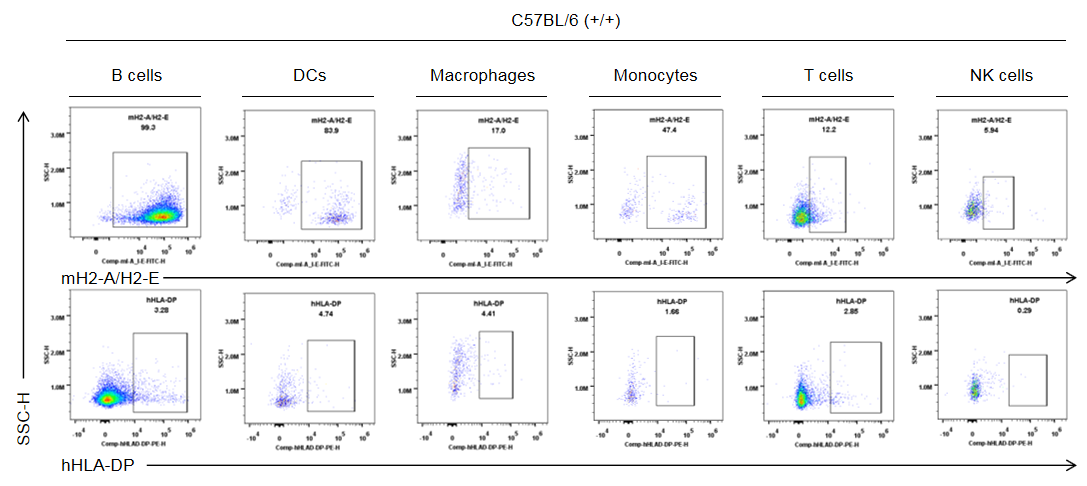
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Mouse H2-A/H2-E was only detectable in wild-type mice. Human HLA-DP was not detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the spleen of B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice
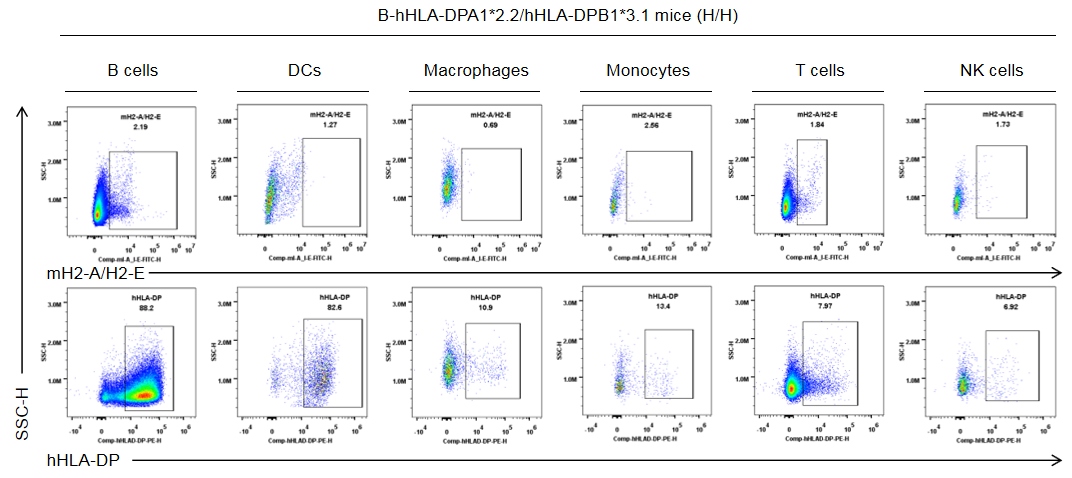
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Human HLA-DP was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the blood of B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice
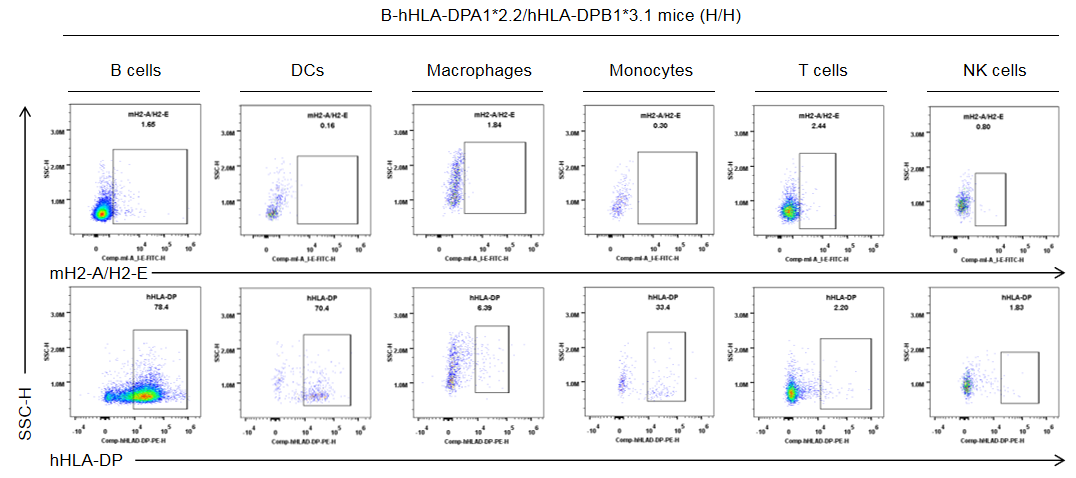
Strain specific HLA-DP expression analysis in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from the homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H). Protein expression was analyzed with anti-human HLA-DP antibody (BD, 566825) and anti-mouse I-A/I-E antibody (Biolegend, 107606) by flow cytometry. Human HLA-DP was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice, but not in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the spleen
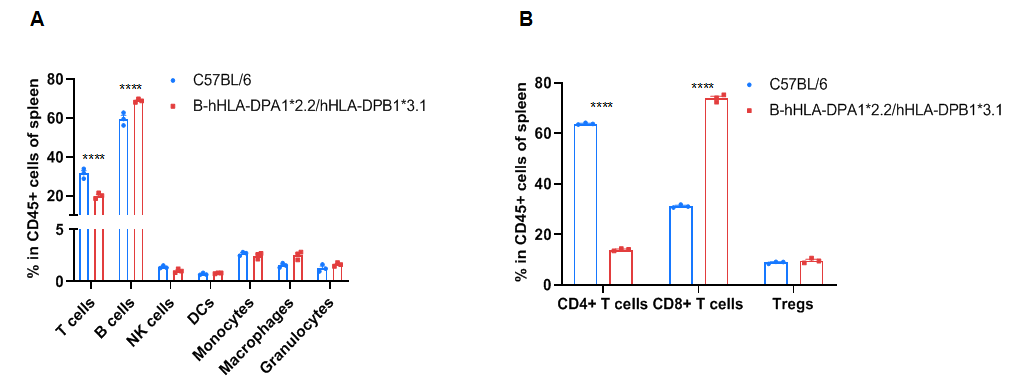
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) (male, n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H) (male, n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of NK cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of T cells and CD4+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were lower than those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of B cells and CD8+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were higher than those in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the lymph node
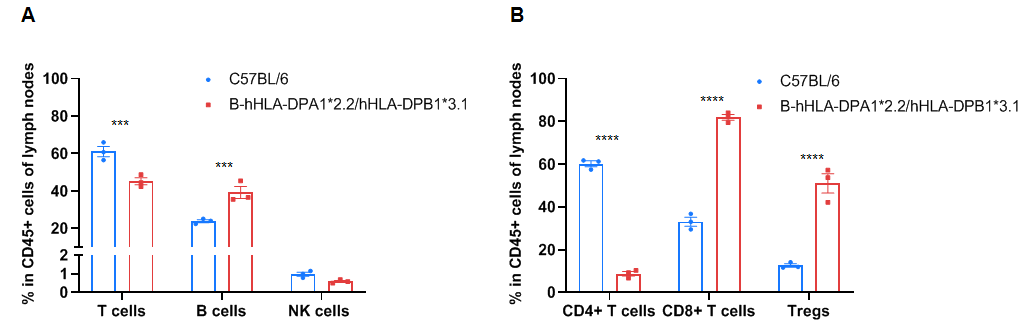
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the lymph node by flow cytometry. The lymph node cells were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) (male, n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H) (male, n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of NK cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of T cells and CD4+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were lower than those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of B cells, CD8+ T cells, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were higher than those in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the blood
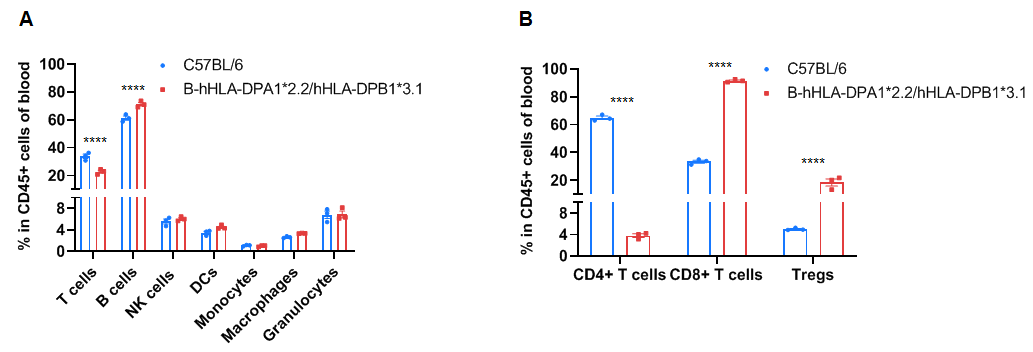
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the blood by flow cytometry. Blood cells were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) (male, n=3, 6-week-old) and homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (H/H) (male, n=3, 6-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of NK cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of T cells and CD4+ T cells in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were lower than those in C57BL/6 mice. Percentages of B cells, CD8+ T cells, and Tregs in homozygous B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice were higher than those in C57BL/6 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
The peptide induced immune responses in B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice
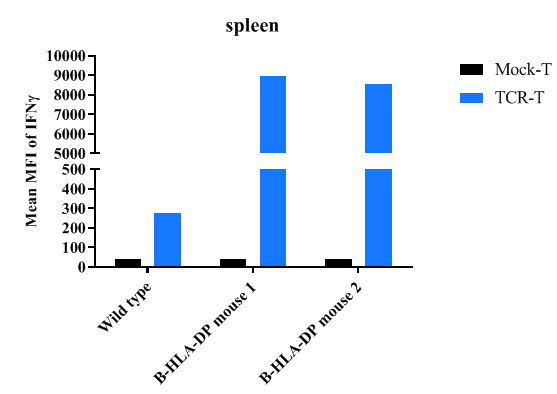
Detection of peptide-induced immune responses in B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice by IFN-γ ELISpot assay. Female C57BL/6 mice (n=1) and B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice (n=2) at the age of 11 weeks were inoculated the peptide at the inside muscle of both legs. One week after the last immunization, mice were sacrificed. The splenocytes were isolated and used as antigen presenting cell. Briefly, spleen cells were loaded with the antigen peptide for 2hrs and washed for co-culture assay. And then the peptide loaded spleen cells were co-cultured with engineered Mock-T or TCR-T cells for overnight for measuring the IFN-γ secretion by ELISA method, respectively. The results demonstrate that the negative control Mock-T cells can’t induce immune responses while the positive group TCR-T cells induce obvious responses in B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice.
Note: This experiment was performed by the client using B-hHLA-DPA1*2.2/hHLA-DPB1*3.1 mice. All the other materials were provided by the client.



















 京公网安备:
京公网安备: