|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Pdcd1tm1(PDCD1)BcgenCd274tm1(CD274)Bcgen
Tnfrsf9tm1(TNFRSF9)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
130569
|
Related Genes
|
PD-1(Programmed death-1)
NFRSF9(TNF receptor superfamily member 9, also known as 4-1BB)
|
NCBI Gene ID
|
18566,60533,21942
|
Protein expression analysis
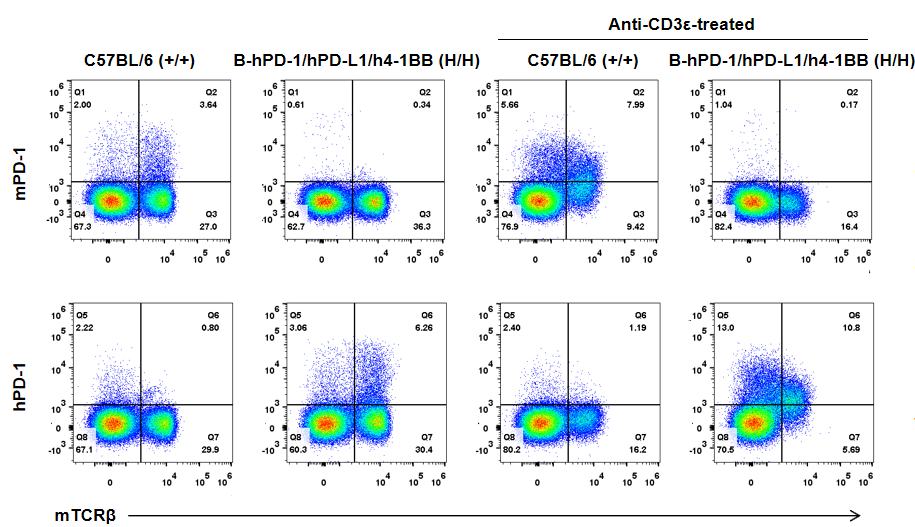
Strain specific PD-1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type C57BL/6 (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-PD-1 antibody. Mouse PD-1 was detectable in wild type C57BL/6 mice but not homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Human PD-1 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice but not in wild type C57BL/6 mice.
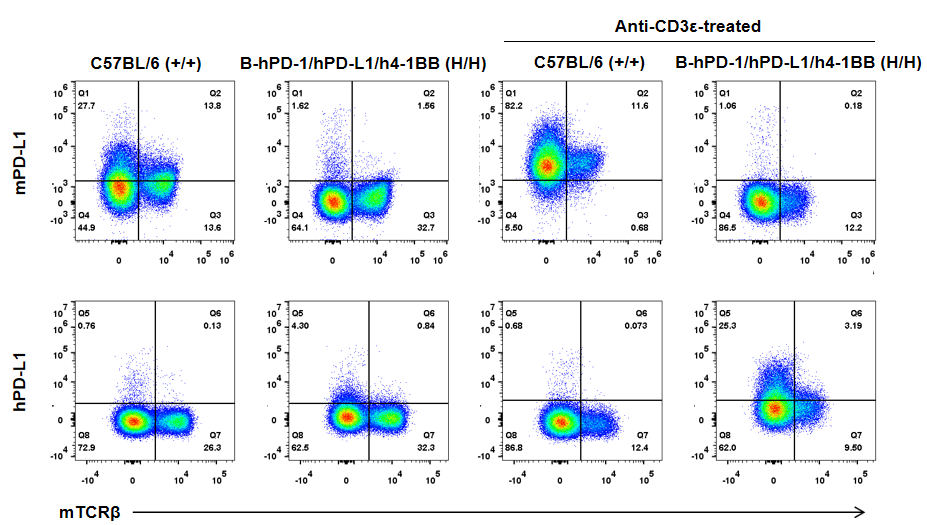
Strain specific PD-L1 expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-PD-L1 antibody. Mouse PD-L1 was detectable in wild type C57BL/6 mice but not homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Human PD-L1 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice but not in wild type C57BL/6 mice.
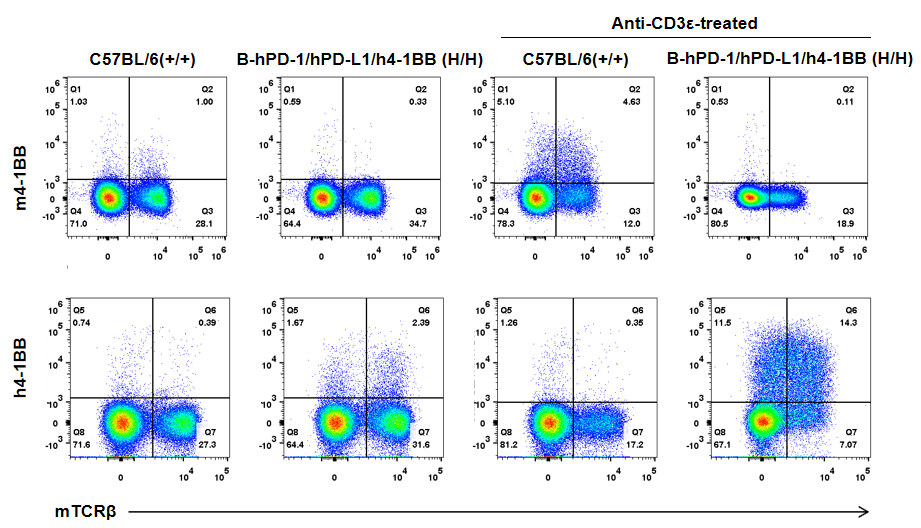
Strain specific 4-1BB expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild type (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-4-1BB antibody. Mouse 4-1BB was detectable in wild type C57BL/6 mice but not homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Human 4-1BB was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice but not in wild type C57BL/6 mice.
Analysis of blood,spleen and lymph node leukocytes cell subpopulations
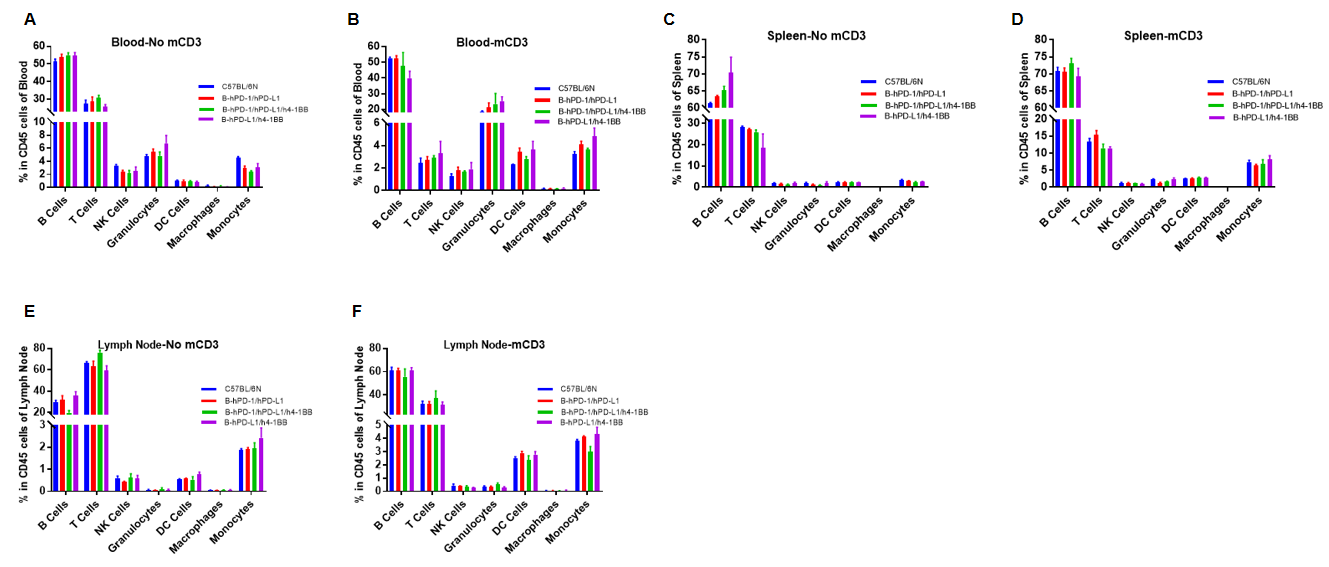
Analysis of blood,spleen and lymph node leukocytes cell subpopulations by FACS
Blood, spleen and lymph node leukocytes cell were isolated from female mice in the panel(n=3, 6 week-old). Flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, Granulocytes, monocytes, DC and macrophage cells in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1, B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB and B-hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice both at rest and in stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, demonstrating that the humanized mouse does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood,spleen and lymph node.
Analysis of blood,spleen and lymph node T cell subpopulations
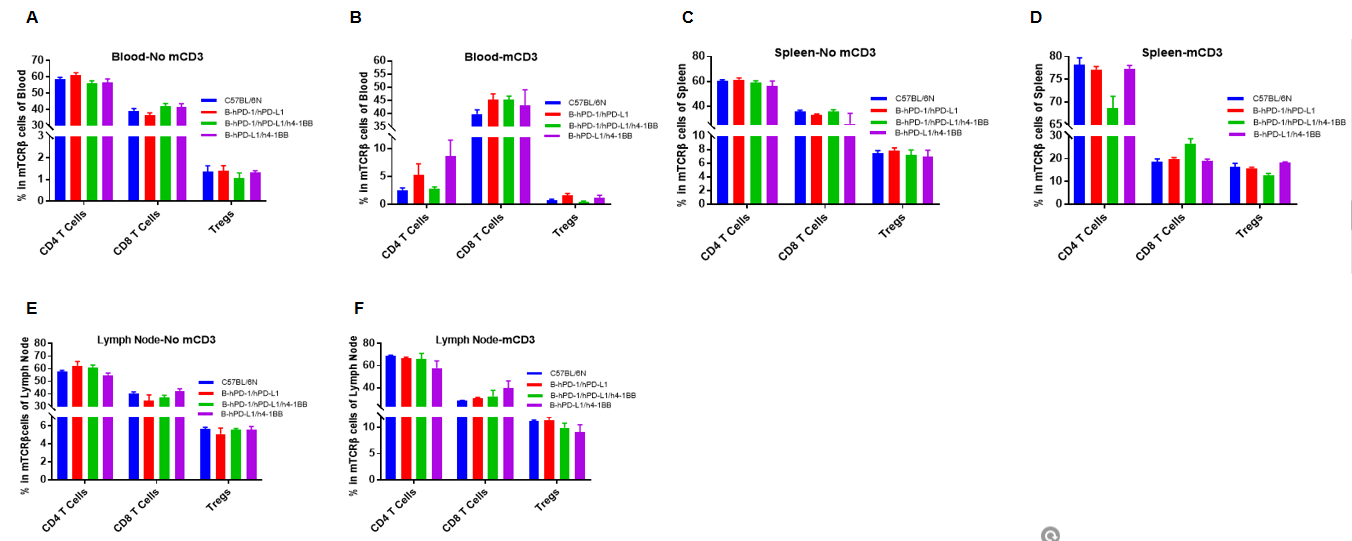
Analysis of blood,spleen and lymph node T cell subpopulations by FACS
Blood, spleen and lymph node leukocytes cell were isolated from female mice in the panel(n=3, 6 week-old). Flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. Percent of CD4+T cells, CD8+T cells and Tregs in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1, B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB and B-hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice both at rest and in stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo, demonstrating that the humanized mouse does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood, spleen and lymph node.
Blood routine test results
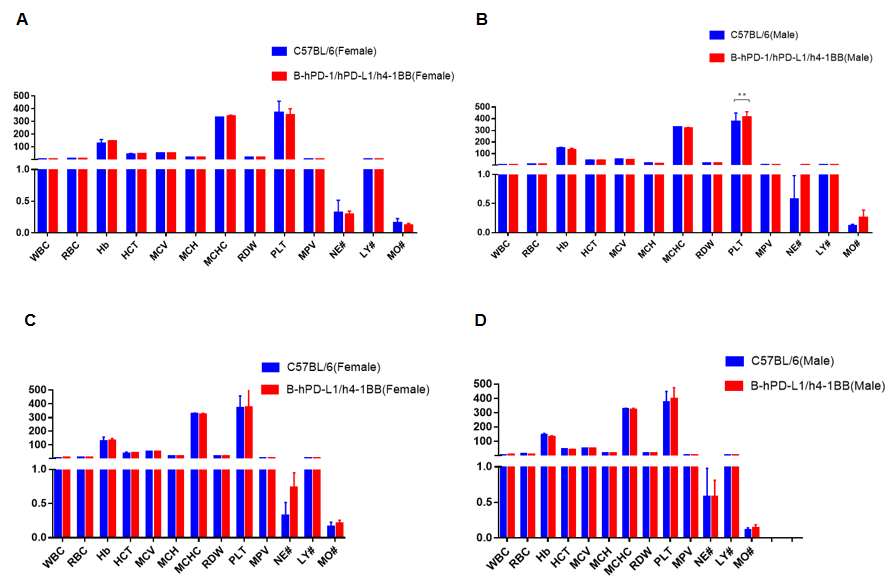
Complete blood count (CBC). Blood from C57BL/6, B-hPD-L1/h4-1BB and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (n=5, 6 week-old, female and male) ) were collected and analyzed for CBC. Any measurement of B-hPD-L1/h4-1BB and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice in the panel were similar to C57BL/6, and there was no differences between male and female mice, indicating that humanized mouse does not change blood cell composition and morphology. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Blood chemistry results
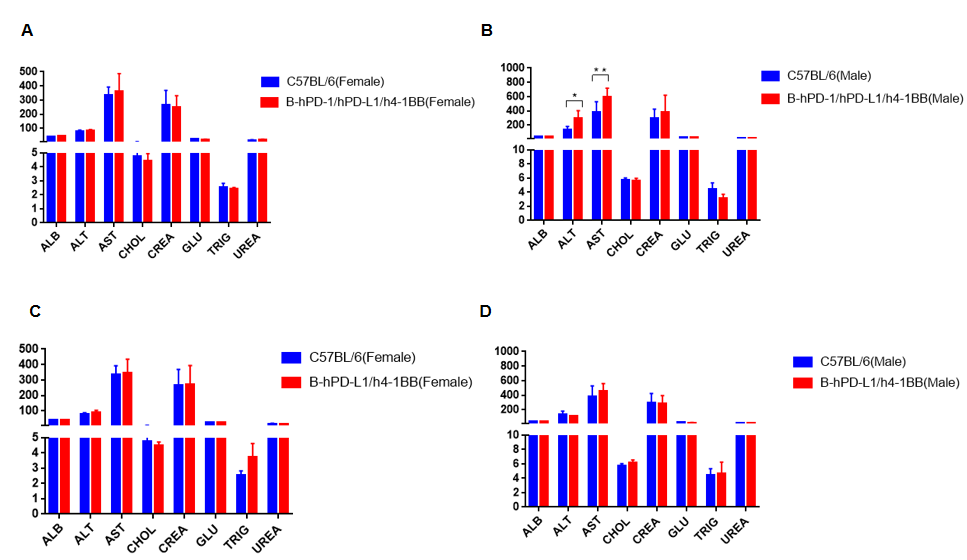
Blood chemistry tests of B-hPD-L1/h4-1BB and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Serum from C57BL/6, B-hPD-L1/h4-1BB and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (n=5, 6 week-old, female and male) were collected and analyzed for levels of ALT, AST and other indicators in the panel. There was no differences on either measurement between C57BL/6 and humanized mouse, indicating that humanized mouse does not change ALT and AST levels or health of liver. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Combination therapy of anti-human PD-L1 antibody and anti-human 4-1BB antibody
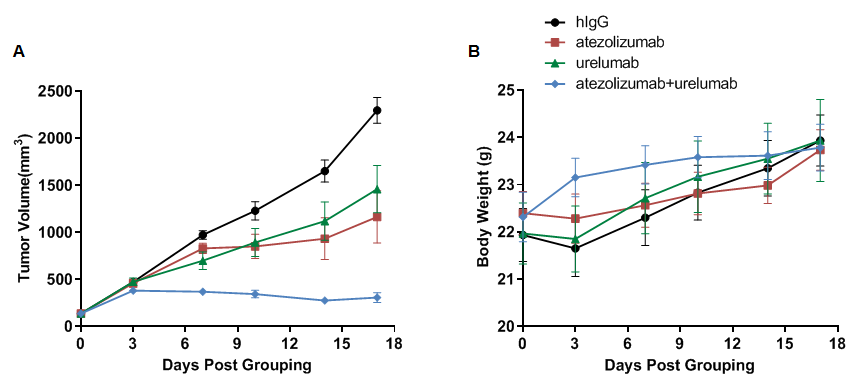
Antitumor activity of anti-human PD-L1 antibody combined with anti-human 4-1BB antibody in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human PD-L1 antibody (in house) combined with anti-human 4-1BB antibody (in house) inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hPD-L1 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with human PD-L1 and human 4-1BB antibodies in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
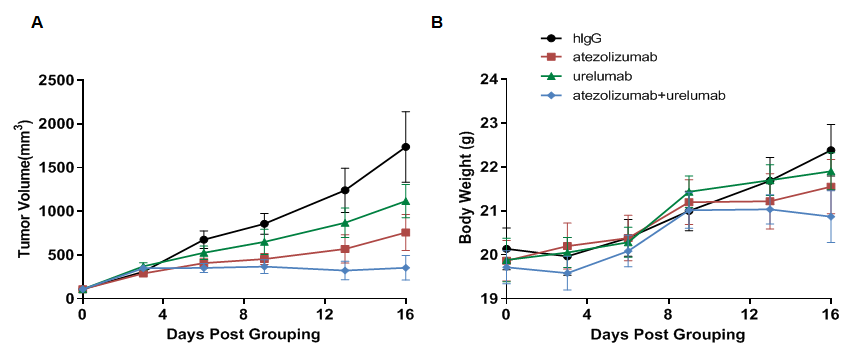
Antitumor activity of anti-human PD-L1 antibody combined with anti-human 4-1BB antibody in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. (A) Anti-human PD-L1 antibody (in house) combined with anti-human 4-1BB antibody (in house) inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hPD-L1 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (female, 6-7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with human PD-L1 and human 4-1BB antibodies in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies
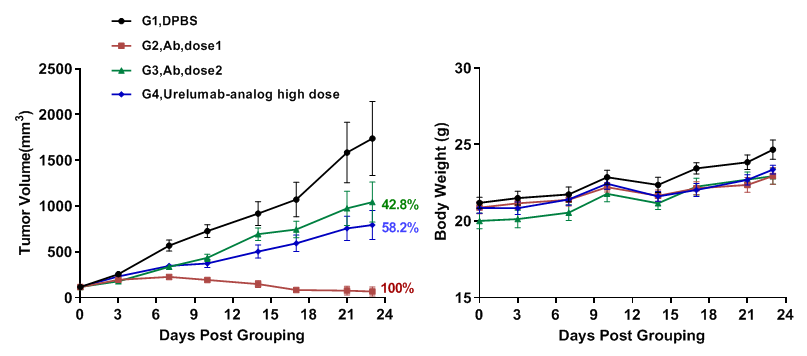
Antitumor activity of 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. (A) anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies inhibited MC38-hPD-L1 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. Murine colon cancer MC38-hPD-L1 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibodies in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, the antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth with dose-dependent in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies show varied leukocytes subpopulations in tumor
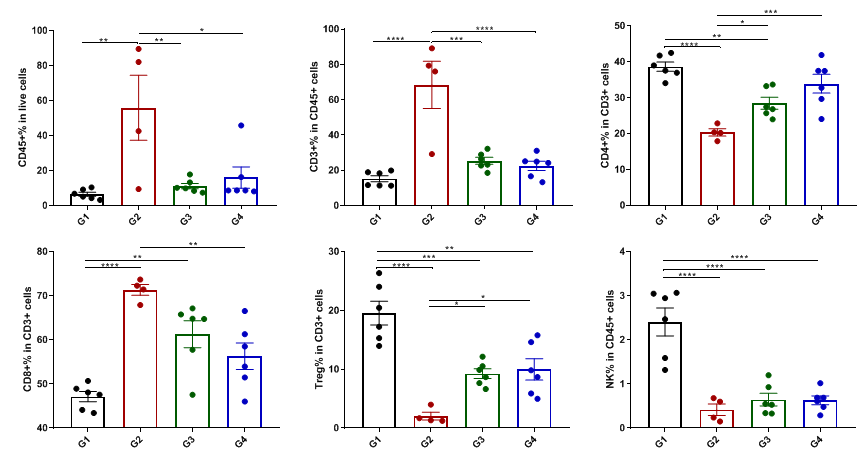
Anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies show varied leukocytes subpopulations in tumor.
Tumors were harvested at the endpoint of the experiment from groups described in the previous page, and flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess infiltrating leukocyte subpopulations. In the group G2, treated with anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies with high dose, shows a significant increase in the percent of CD45+ cells , CD3+ T cells and CD8+ T cells. Meanwhile, the percent of CD4+ T cells and Tregs decreased. The same results were not seen in the other groups, demonstrating that the 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies leading to more cytotoxic T cells activation and infiltration into the tumors, which is important in the tumor killing mechanism. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies show varied leukocytes subpopulations in tumor
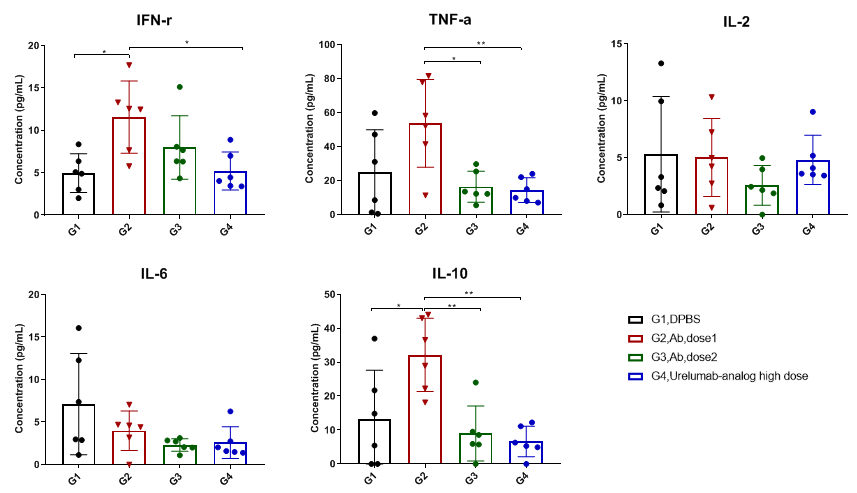
Anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies therapies led to changed cytokine profile in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice.
Serum was harvested at the endpoint of the experiment from groups, as indicated on the graph (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Serum cytokine levels were analyzed at 48 hours after last dosing on day 23. 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies with high dose resulted in a significant increase of IFN-γ and IL10 in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice. The same results were not seen in the other groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
High dose of 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies resulted in liver toxicity
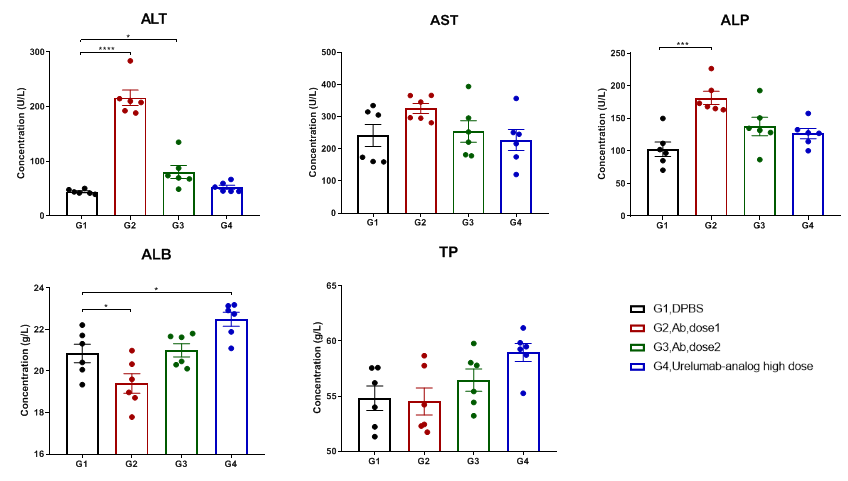
High-dose anti-human 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies caused significant increases of ALT in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/h4-1BB mice.
Serum was harvested at the endpoint of the experiment from groups, as indicated on the graph (female, 7-week-old, n=6). Blood chemistry tests were performed at 48 hours after last dosing on day 23. 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies in high dose caused significant increase of ALT and ALP compared with DPBS control, while had no effect in other groups, demonstrating that the 4-1BB×PD-L1 bispecific antibodies may lead to liver toxicity. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (ALT: alanine transaminase, AST: aspartate transaminase, ALP: alkaline phosphatase, ALB: Albumin, TP: total protein)























 京公网安备:
京公网安备: