| Strain Name |
NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Bcgen Sirpatm1(SIRPA)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name |
B-NDG hSIRPA mice |
| Background | B-NDG | Catalog number | 110604 |
|
Related Genes |
SIRPα (signal regulatory protein alpha) |
||
|
NCBI Gene ID |
19261 | ||
Description
Signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) is a transmembrane protein with an extracellular region comprising three Ig-like domains and a cytoplasmic region containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs which mediate binding of the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP1 and SHP2. SIRPα is especially abundant in myeloid cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells(DC), whereas it is expressed at very low levels in T, B ,NK, and NK T cells. SIRPα inhibits phagocytosis in macrophages upon interacting with its ligand CD47, which is commonly upregulated on the surface of malignant cells. Thus, antibodies that block the CD47-SIRPα interaction should enhance macrophage phagocytosis in the tumor microenvironment and inhibit tumor growth, making anti-SIRPα antibodies promising tools for cancer immunotherapy.
Biocytogen developed the B-NDG hSIRPA mice, and the targeting strategy was that the exon 2 of mouse Sirpα gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human SIRPα exon 2 in B-NDG hSIRPA mice. This mouse combines a B-NDG mouse background (completely lacking mature T, B and NK cells and were deficient in cytokine signaling) and expresses human SIRPα protein extracellular domain. In homozygous mice, mouse SIRPα were absent and only human protein expression was detected. B-NDG hSIRPA mice paired with genetically modified Raji-luc cancer cells were used to evaluate the efficacy of antibodies targeting SIRPα. Anti-human SIRPα antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-NDG hSIRPA mice. Humanized B-NDG hSIRPA mice are a promising in vivo efficacy model for the development of SIRPα antibodies that can be advanced to human clinical trials.
General information
Antitumor mechanisms of anti-CD47 antibodies
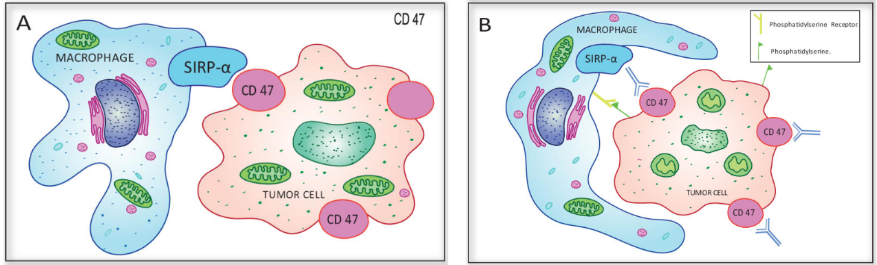
The antitumor mechanisms of anti-CD47 antibodies. A. CD47-SIRPα interaction blocks macrophage phagocytosis of cancer cells. B. Cancer cells treated with anti-CD47 antibody leads to type-III PCD (actin rearrangement, mitochondrial swelling and damage, exposure of phosphatidylserine on plasma membrane) along with induction of phagocytosis by macrophages.
Generation of gene editing mouse model and expression analysis
Protein expression analysis (heterozygous mice)
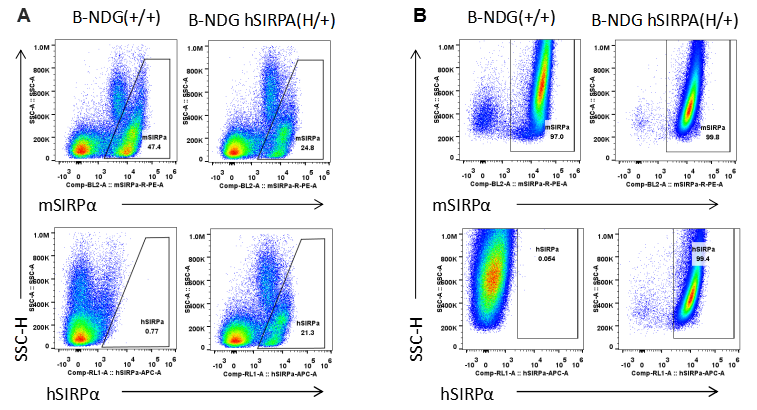
Species specific SIRPα expression analysis in B-NDG hSIRPA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes (A) and peritoneal lymphocyte (B) from B-NDG and heterozygous B-NDG hSIRPA (H/+) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-SIRPα antibodies. Mouse SIRPα was detectable in B-NDG and heterozygous B-NDG hSIRPA mice. Human SIRPα were exclusively detectable in heterozygous B-NDG hSIRPA but not B-NDG mice.
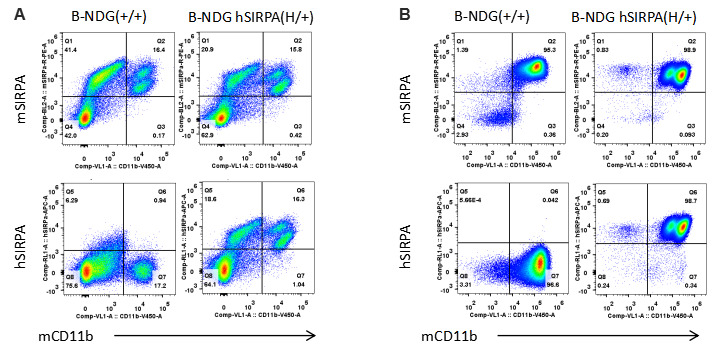
Species specific SIRPα expression analysis in B-NDG hSIRPA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes (A) and peritoneal lymphocyte (B) from B-NDG and heterozygous B-NDG hSIRPA (H/+) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-SIRPα and anti-CD11b antibodies. Mouse SIRPα were detectable in macrophages of B-NDG and heterozygous B-NDG hSIRPA mice. Human SIRPα were exclusively detectable in macrophages of heterozygous B-NDG hSIRPA but not B-NDG mice.
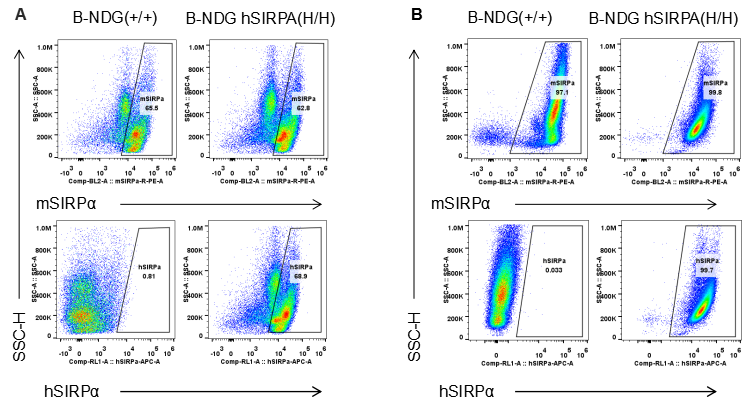
Species specific SIRPα expression analysis in B-NDG hSIRPA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes (A) and peritoneal lymphocyte (B) from B-NDG and homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA (H/H) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-SIRPα antibodies. Mouse SIRPα was detectable in B-NDG and homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA mice. This anti-mouse SIRPα antibody also cross reacts with human SIRPα. Human SIRPα were exclusively detectable in homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA but not B-NDG mice.
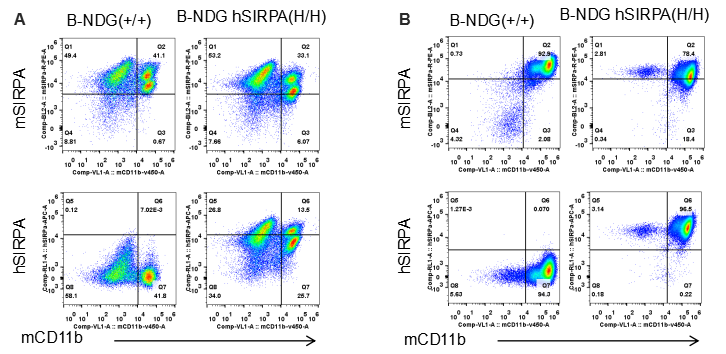
Species specific SIRPα expression analysis in B-NDG hSIRPA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes (A) and peritoneal lymphocyte (B) from B-NDG and homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA (H/H) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry with anti-SIRPα antibodies. Mouse SIRPα was detectable in macrophages of B-NDG and homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA mice. This anti-mouse SIRPα antibody also cross reacts with human SIRPα. Human SIRPα were exclusively detectable in macrophages of homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA but not B-NDG mice.
Analysis of spleen leukocytes cell subpopulations in B-NDG hSIRPA mice
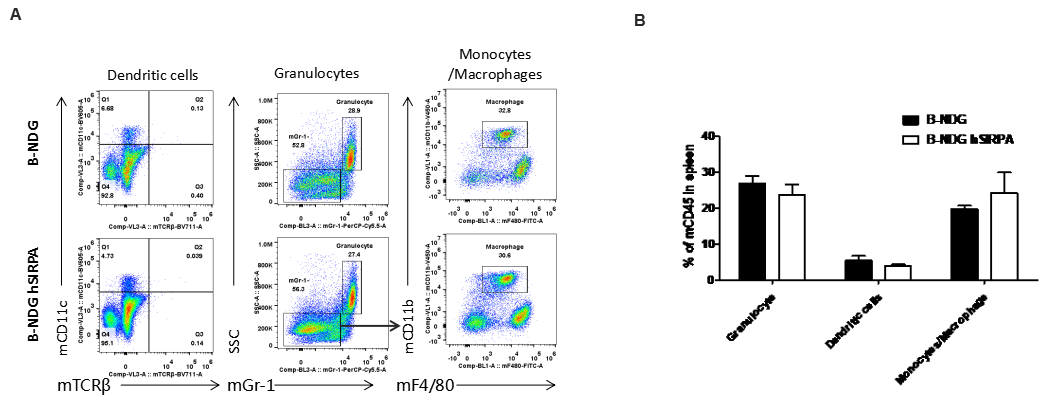
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS
Splenocytes were isolated from male B-NDG and B-NDG hSIRPA mice (n=3, 7-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for CD45 population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of Monocyte, DC and macrophage cells in homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA mice were similar to those in the B-NDG mice, demonstrating that introduction of hSIRPα in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen.
B-NDG hSIRPA mice can effectively evaluate the in vivo efficacy of anti-human CD47 antibody
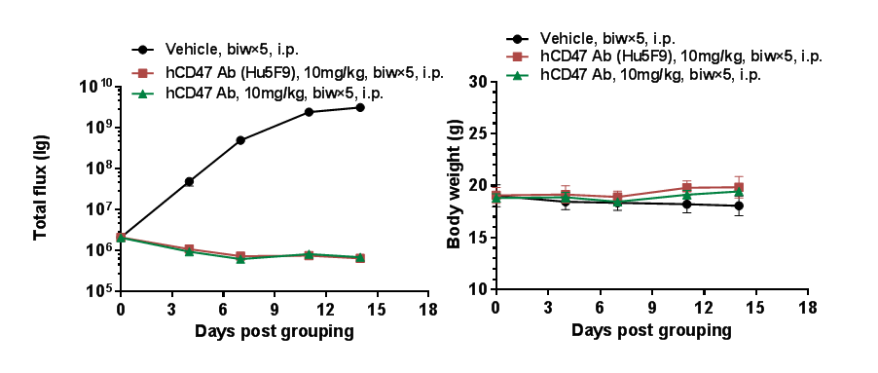
B-luc-GFP Raji cells (5E5), a human Burkitt lymphoma overexpressing luciferase-GFP, were injected into B-NDG hSIRPA mice intravenously (female, 5 weeks old, n = 5). The changes in fluorescence intensity were detected twice weekly using a small animal imager. Mice were grouped when fluorescence intensity reached 1E6 p/sec and treated with anti-human CD47 antibody. (A) Fluorescence intensity changes; (B) Body weight changes. The results showed that anti-human CD47 antibody could significantly inhibit tumor growth in B-NDG hSIRPA mice.
Combination of anti-hSIRPA antibody and anti-hCD20 antibody can effectively inhibit the tumor growth in B-NDG hSIRPA mice
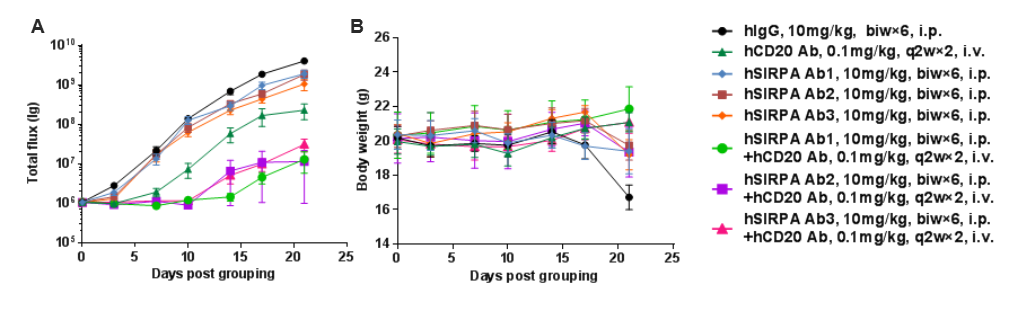
B-luc-GFP Raji cells (1E5), a human Burkitt lymphoma overexpressing luciferase-GFP, were inoculated into B-NDG hSIRPA mice (female, 8 weeks old, n = 6) intravenously. The changes in fluorescence intensity were detected twice weekly using a small animal imager. Mice were grouped when fluorescence intensity reached approximately 1E6 p/sec and treated with anti-human SIRPA antibody and anti-human CD20 antibody. (A) Fluorescence intensity changes; (B) Body weight changes. The results showed that the combination of anti-human SIRPA antibody and anti-human CD20 antibody significantly inhibited tumor growth in B-NDG hSIRPA mice.
Summary
- Species specific SIRPα expression analysis in B-NDG hSIRPA mice by flow cytometry. Human SIRPα were exclusively detectable in macrophages of homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA
- Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Percent of Monocyte, DC and macrophage cells in homozygous B-NDG hSIRPA mice were similar to those in the B-NDG mice. demonstrating that introduction of hSIRPα in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen.
- Combination of hSIRPA and hCD20 antibodies shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups in B-NDG hSIRPA mice










 京公网安备:
京公网安备: