Common name
|
B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38
|
Catalog number
|
322295
|
|
Aliases
|
EGFR, ERBB, ERBB1, ERRP, HER1, NISBD2,
PIG61, mENA, epidermal growth factor receptor
|
Disease
|
Colon carcinoma
|
Organism
|
Mouse
|
Strain
|
C57BL/6
|
|
Tissue types
|
Colon
|
Tissue
|
Colon
|
Description
-
Origin: The MC38 cell line is derived from C57BL6 murine colon adenocarcinoma cells. The cell line is a commonly used murine model for colorectal carcinoma.
-
Background Information: EGFR is widely distributed on the surfaces of epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and other cell types in mammals. It is activated by binding to ligands such as EGF, leading to dimerization. The activation of EGFR can promote the growth and differentiation of various cells, including during embryonic development, the maintenance and repair of adult tissues, as well as the proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells. EGFR is one of the most classic targets in the field of anti-tumor therapy. EGFR-targeted drugs use various mechanisms to inhibit EGFR activation, suppress the EGFR signaling pathway, and thereby block cellular signal transduction, ultimately inhibiting the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells.
-
Gene targeting strategy: The expression cassette containing an exogenous promoter, the extracellular region of human EGFR, and the transmembrane and intracellular regions of mouse Egfr was randomly inserted into the genome of B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells.
-
Tumorigenicity: Confirmed in B-hEGFR mice and B-h4-1BB/hEGFR mice.
-
Application: The B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 tumor models can be used for preclinical evaluation of The B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 tumor models can be used for preclinical evaluation of anti-human EGFR antibodies.
-
Notes:
-
B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 #1-E02 can not establish tumors in wild-type C57BL/6 mice, and only in EGFR related humanized mice.
-
B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells simultaneously express humanized EGFR and EGFP. If detecting the expression of humanized EGFR, it is necessary to choose an appropriate flow channel.
Protein expression analysis
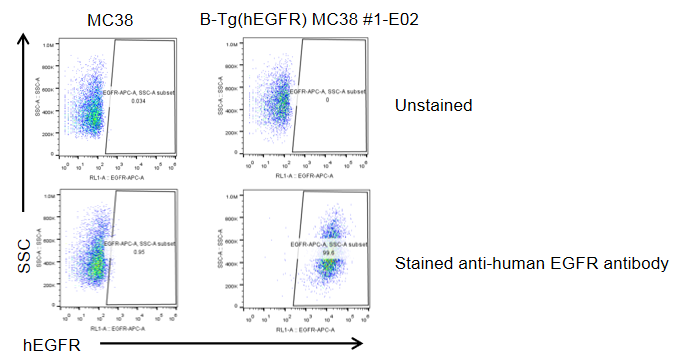
EGFR expression analysis in B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells by flow cytometry. Single cell suspensions from wild-type MC38 and B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cultures were stained with species-specific anti-EGFR antibody. Human EGFR was detected on the surface of B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells but not wild-type MC38 cells. The 1-E02 clone of B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells was used for in vivo tumor growth assays.
Tumor growth curve & body weight changes

Subcutaneous tumor growth of B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells. B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells (5x105) and wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hEGFR mice (female, 6-9 weeks-old, n=6). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume. (B) Body weight. Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 X long diameter X short diameter2. Results indicate that B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Protein expression analysis of tumor tissue
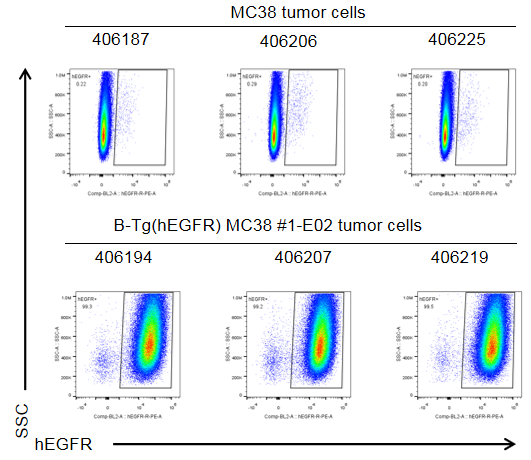
EGFR expression evaluated on B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 tumor cells by flow cytometry. B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells were subcutaneously transplanted into homozygous B-hEGFR mice (n=6). Upon conclusion of the experiment, tumor cells were harvested and analyzed with anti-human EGFR antibody by flow cytometry. As shown, human EGFR was highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Therefore, B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells can be used for in vivo efficacy studies evaluating novel EGFR therapeutics.
Tumor growth curve & body weight changes
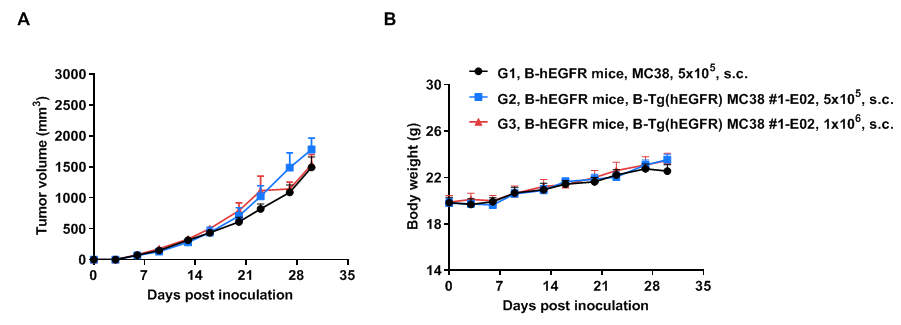
Subcutaneous tumor growth of B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells. B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells (5x105, 1x106) and wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hEGFR mice (female, 5-8 weeks-old, n=6). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume. (B) Body weight. Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 X long diameter X short diameter2. Results indicate that B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Tumor growth curve & body weight changes
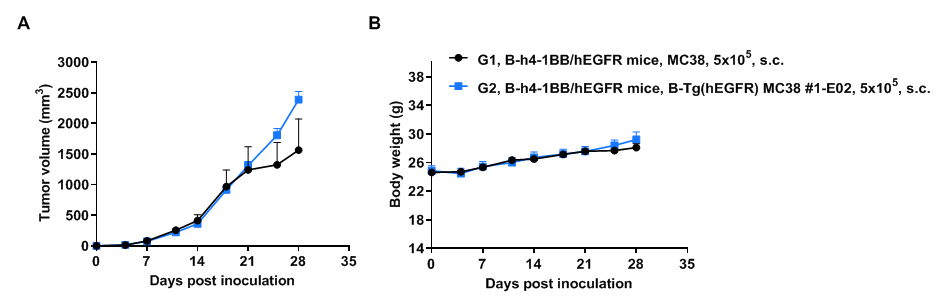
Subcutaneous tumor growth of B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells. B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells (5x105) and wild-type MC38 cells (5x105) were subcutaneously implanted into heterozygous B-h4-1BB/hEGFR mice (male, 6 weeks-old, n=5). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice a week. (A) Average tumor volume. (B) Body weight. Volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V=0.5 X long diameter X short diameter2. Results indicate that B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells were able to establish tumors in vivo and can be used for efficacy studies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human EGFR antibodies
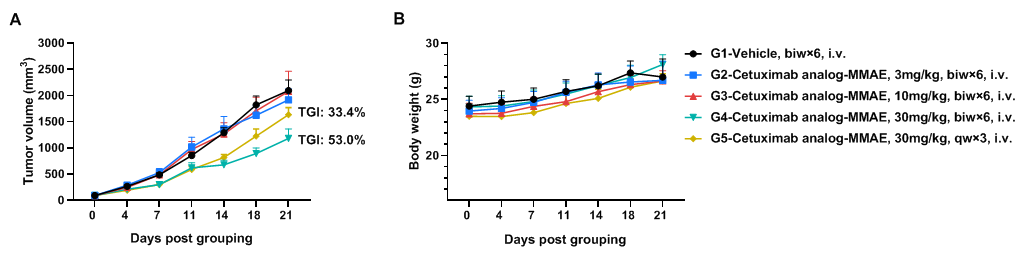
Antitumor activity of anti-human EGFR antibody in B-hEGFR mice. (A) Anti-human EGFR antibody inhibited B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 tumor growth in homozygous B-hEGFR mice. Murine colon cancer B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hEGFR mice (female, 6-8 weeks-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 50-150 mm3, at which time they were intravenous injected with anti-human EGFR ADC cetuximab analog-MMAE (in house) indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, 30mg/kg anti-human EGFR ADC cetuximab analog-MMAE (in house) treatment group was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hEGFR mice, demonstrating that the B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human EGFR antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human EGFR antibodies-individual tumor growth curves
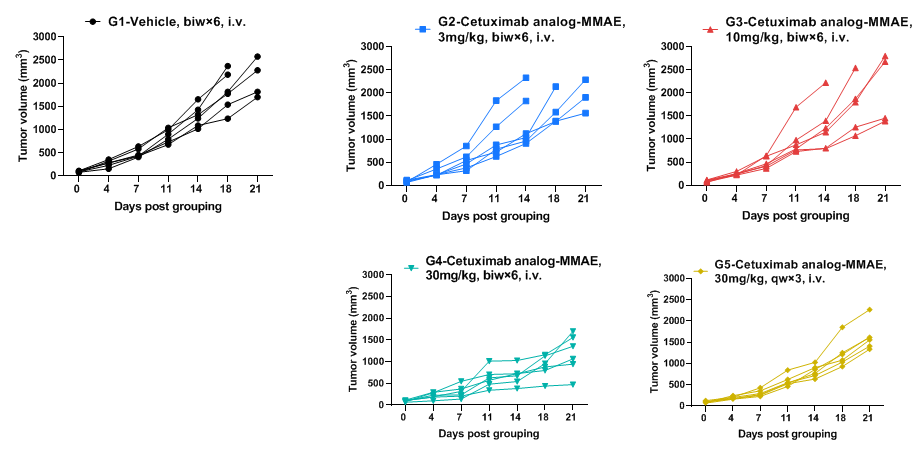
Antitumor activity of anti-human EGFR antibody in B-hEGFR mice. Anti-human EGFR antibody inhibited B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 tumor growth in homozygous B-hEGFR mice. Murine colon cancer B-Tg(hEGFR) MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hEGFR mice (female, 6-8 weeks-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 50-150 mm3, at which time they were intravenous injected with anti-human EGFR ADC cetuximab analog-MMAE (in house) indicated in panel.

















 京公网安备:
京公网安备: